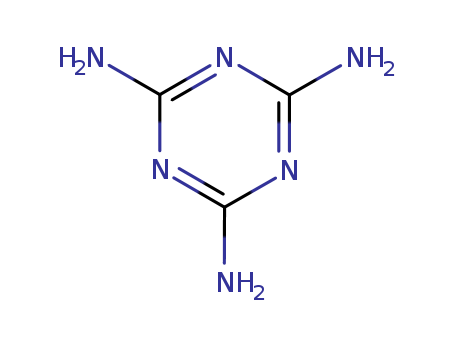
CasNo: 108-78-1
Molecular Formula: C3H6N6
Appearance: white solid
|
|
|
|
Industrial Applications |
Melamine is widely used in various industrial applications, including adhesives, plastics, flame retardants, cleaners, polymer resins, fertilizers, and catalysis. It is utilized in wood panels, paints, coatings, foam seating, mattresses, automotive brake tubes, and hoses. |
|
Health Risks and Regulatory Status |
Melamine has been classified as "carcinogenic to humans" and may cause damage to organs, particularly the urinary tract, through prolonged or repeated exposure. It is considered a potential groundwater contaminant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends daily melamine intake to be less than 0.2 mg/kg body weight per day. |
|
Industrial and Domestic Uses |
Melamine is utilized in paints, coatings, foam seating, bedding, plasticizers in concrete, automobile brake tubes, and hoses. It is also used in thermally fused melamine paper, whiteboards, flakeboards, sealants, inkjet ink, and melamine-formaldehyde resins for laminates, coatings, plastics, adhesives, and dishware. |
|
Detection Methods |
Standard methods for detecting melamine in milk involve chromatographic techniques, which are expensive and time-consuming. Alternative techniques such as infrared, Raman, and UV spectrometry are also employed for melamine detection in milk, providing faster and potentially more cost-effective options. |
|
Production Methods |
The compound now is synthesized from urea. |
|
Preparation |
The standard route to melamine is from urea. Urea is heated in the presence of ammonia at 250-350°C and 4--20 MPa. The reaction probably involves the simultaneous dehydration and hydration of urea to form cyanamide and ammonium carbamate; trimerization of the cyanamide then leads to melamine:Thus only 50% of the urea used gives melamine in one step and ammonium carbamate has to be separated and converted to urea for recycling. Despite this limitation, the urea route is the most economical of currently available routes. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A trimer of cyanamide, with a 1,3,5-triazine skeleton. |
|
General Description |
Colorless to white monoclinic crystals or prisms or white powder. Sublimes when gently heated. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Melamine is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong acids . Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. |
|
Hazard |
Toxic by ingestion, skin, and eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Literature sources indicate that Melamine is nonflammable. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Contact allergens |
Melamine-formaldehyde resin (MFR) results from condensation of melamine and formaldehyde. It is anactive ingredient of strong (reinforced) plasters, such as industrial or some dental plasters used for molding.It is also used as a textile finish resin. MFR acts as an allergen generally because of formaldehyde releasing (see Chap. 40) |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. An eye, skin, and mucous membrane irritant. Causes dermatitis in humans. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx and CN-. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Manufactured from urea, melamine is used in the manufacture of plastics, melamineformaldehyde resins; rubber, synthetic textiles; laminates, adhesives, and molding compound |
|
Carcinogenicity |
A bioassay of melamine was conducted in rats and mice by NTP. Male F344 rats and B6C3F1 mice were administered melamine in their diets at concentrations of 2250 or 4500 ppm daily for 103 weeks.Female rats were fed 4500 or 9000 ppm melamine. At the end of 111 weeks, surviving animals were killed and examined. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise Melamine from water or dilute aqueous NaOH. It sublimes at ~240o on prolonged heating. [Beilstein 26 I 74, 26 II 132, 26 III/IV 1253.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Melamine neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. |
InChI:InChI=1/C3H8N6/c4-2-1-3(5)8-9(6)7-2/h1,7H,4,6H2,(H2,5,8)
-
-
-
Five inorganic salts of biguanide with c...
-
-
-
The unusually high heats of vaporization...
Polymeric carbon nitride (CN) semiconduc...
-
Abstract: A Pd–C3N4@titanate nanotube (P...
-
Poly(triazine imide)-based carbon nitrid...
2,4,6-Triureido-1,3,5-triazine and 2-ami...
In this study, we synthesized a novel vi...
The invention provides a dicyandiamide p...
Urea appears to be a key intermediate of...
A process is described, having a low-ene...
guanidine nitrate

malononitrile

2,4,6-triaminopyrimidine

2,4,6-triamino-s-triazine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 100 ℃;
|
malonic acid

guanidine nitrate

urea

2,4,6-triaminopyrimidine

2-aminopyrimidine-4,6-diol

BARBITURIC ACID

2,4,6-triamino-s-triazine

pyrimidine-2,4,5-triamine

C4H4N2O3*C4H5N3O2

2,6-diaminopyrimidin-4-ol

4,6-diamino-2-hydroxypyrimidine

Malonamic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 65 ℃; for 120h;
|
1,3,5-trichloro-2,4,6-triazine
cyanuric bromide
2,4,6-tris(methylthio)-1,3,5-triazine
BIURET
bis(hydroxymethyl)melamine
2,4-diamino-6-hydroxymethylamino-1,3,5-triazine
[1,3,5]triazine-2,4,6-triyltriamino-tris-methanol
hexa(hydroxymethyl)melamine