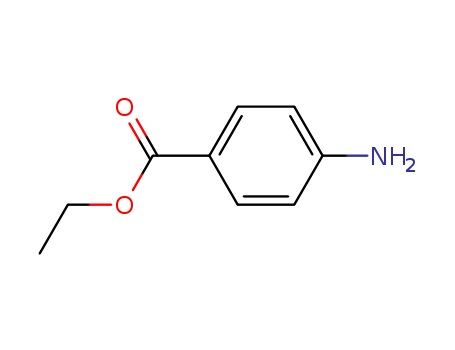
CasNo: 94-09-7
Molecular Formula: C9H11NO2
Appearance: white odourless crystals
|
Indications and Usage |
Benzocaine is a colorless trapezial crystal. Its melting point is 92℃ (88-90℃), boiling point is 183-184°C (1.87kPa). 1g of this drug is soluble in about 2500ml water, 5ml ethanol, 2ml chloroform, 4ml ether or 30-50ml almond oil and olive oil, and it is also soluble in dilute acid. It is stable in air, odorless, and slightly bitter. Benzocaine is a lipid-soluble surface anesthetic, and it weaker than other local anesthetics such as lidocaine and tetracaine, so it will not cause any discomfort due to its anesthetizing effects when acting on mucosa. Benzocaine is a type of drug with relatively strong lipid-solubility and will bind with mucosa and the fatty layer of skin, but it will not easily penetrate into the body and cause poisoning. Benzocaine can be used as a precursor for Ossur imitation, orthocaine, and procaine. It is also used as a local anesthetic and can stop pain and itching. It is mainly used in pain and itch prevention on wounds, ulcer surfaces, mucous membrane surfaces and hemorrhoids. Its paste form can also lubricate and stop pain for the nasopharynx and endoscope. Benzocaine’s aural solution is used to alleviate acute congestion, concentrated otitis externa, and the pain and itching of swimming otitis. Benzocaine is also effective for toothaches, sore throat, oral ulcers, all kinds of hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and vulvar itching. Benzocaine can be used as a male sex organ numbing agent to slow ejaculation. It can also be used as a numbing lubricant for the pharynx and endoscope, and it can be used as a UV absorbing agent for cosmetics. |
|
synthesis |
Benzocaine is produced by reduction of ethyl 4-nitrobenzoate with iron or by the acid-catalyzed esterification of 4-aminobenzoic acid with ethanol:In a 5-mL round bottom flask, add 120 mg of 4-aminobenzoic acid (often called PABA for paminobenzoic acid), 1.5 mL of absolute ethanol (absolute ethanol is completely free of water and can be found on the hooded shevles), and 3 boiling chips. Heat this mixture on a sand bath until all the solid dissolves. Cool in ice and then add 0.25 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid dropwise. (One drop at a time.) A large amount of precipitate will form when the sulfuric acid is added, but this will dissolve during the reflux that follows. Attach an air condenser from the microscale kit, and reflux gently for 60- 75 min. Check periodically to be sure that the mixture is refluxing gently, and that the ring of condensation of solvent lies somewhere along the inner surface of the air condenser; loss of solvent will cause overheating and a significant decrease in yield. |
|
Biological Functions |
Benzocaine is a PABA derivative used primarily for topical application to skin and mucous membranes. Its low aqueous solubility allows it to stay at the site of application for long periods. Its minimal rate of absorption after topical administration is associated with a low incidence of systemic toxicity. Benzocaine is contraindicated in patients with known sensitivity to ester-linked anesthetics or PABA-containing compounds. |
|
Synthesis Reference(s) |
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 71, p. 4154, 1949 DOI: 10.1021/ja01180a513Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 29, p. 1443, 1981 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.29.1443 |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Benzocaine is the ethyl ester of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). Benzocaine acts to inhibit the voltage-dependent sodium channels (VDSCs) on the nerve membrane, stopping the propagation of the action potential. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by rectal route: methemoglobinemia/carboxyhemoglobinem ia in infants. A skin irritant and a mild sensitizer. Local contact may cause contact dermatitis. Used as a topical anesthetic and as a sun-screening agent. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx. See also ETHYL ALCOHOL and ESTERS |
|
Synthesis |
Benzocaine is the ethyl ester of 4-aminobenzoic acid (2.3.1). The classic, optimal way of benzocaine synthesis is the reduction of the nitro group of the ethyl ester of 4-nitrobenzoic acid to benzocaine by hydrogen, which generates directly in the reaction medium by the reaction of iron filings with dilute acids [24–26]. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise Benzocaine from EtOH/H2O or EtOH (m 93-94o), and dry it in air. [Beilstein 14 H 422, 14 IV 1129.] |
|
Structure and conformation |
Ethyl aminobenzoate, a para-aminobenzoate derivative (PABA) |
|
Biological Potentials |
Analogs of benzocaine have demonstrated various biological potentials, including antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-cancer properties. |
|
Chemical Reactions and Derivatives |
Electrophilic and nucleophilic reactions of benzocaine are commonly employed to synthesize a library of benzocaine derivatives with diverse biological activities. |
|
Chemical Structure |
Benzocaine, or ethyl 4-aminobenzoate, is an ester derived from 4-aminobenzoic acid. It is widely used as a topical anesthetic, antipruritic drug, allergen, and sensitizer. |
|
Role as an Anesthetic |
Widely used in oral ulcers, ear pain, and dental complications as an anesthetic agent. Along with lidocaine and other local anesthetics, benzocaine is utilized in surgical procedures and acts as a blocker of Na+ channels. |
|
Clinical Efficacy |
Several placebo-controlled studies support the effectiveness of benzocaine in relieving toothache. |
|
Veterinary Use |
Benzocaine has been confirmed as an effective anesthetic for Colossoma macropomum (tambaqui) juveniles, providing rapid immobilization and recovery. It is a cost-effective option compared to other available anesthetic compounds. |
|
Regulatory Considerations |
The FDA has requested additional pivotal studies to determine the efficacy of benzocaine for toothache relief and to assess dose-response between different formulations. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Benzocaine is a benzoate ester having 4-aminobenzoic acid as the acid component and ethanol as the alcohol component. A surface anaesthetic, it is used to suppress the gag reflex, and as a lubricant and topical anaesthetic on the larynx, mouth, nasal cavity, respiratory tract, oesophagus, rectum, urinary tract, and vagina. It has a role as a topical anaesthetic, an antipruritic drug, an allergen and a sensitiser. It is a benzoate ester and a substituted aniline. |
|
Brand name |
Americaine (Fisons); Baby Anbesol (Whitehall-Robins). |
|
General Description |
Benzocaine is a unique local anesthetic because it does notcontain a tertiary amine. The pKa of the aromatic amine is 3.5ensuring that benzocaine is uncharged at physiological pH.Because it is uncharged, it is not water soluble but is ideal fortopical applications. The onset of action is within 30 secondsand the duration of drug action is 10 to 15 minutes. |
InChI:InChI=1/C9H11NO2/c1-2-12-9(11)7-3-5-8(10)6-4-7/h3-6H,2,10H2,1H3/p+1
We have designed and synthesized four ne...
-
Hydrogenation of ethyl p-nitrobenzoate o...
The kinetics of the reduction of p-nitro...
-
Nickel boride catalyst prepared in situ ...
Designing a metal catalyst that addresse...
The invention belongs to the field of me...
Transition metal catalysis that utilizes...
Ethyl 4-bromobenzoate

4,4'-triazenediyl-di-benzoic acid diethyl ester

diethyl biphenyl-4,4'-dicarboxylate

4,4'-Iminobis(benzoesaeureethylester)

p-aminoethylbenzoate

4,4'-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)azobenzene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With copper(l) iodide; sodium azide; N,N`-dimethylethylenediamine; In dimethyl sulfoxide; at 100 ℃; Inert atmosphere;
|
ethyl 4-nitrobenzoate

p-aminoethylbenzoate

4,4'-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)azobenzene

4,4'-azoxy-di-benzoic acid diethyl ester
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With sodium tetrahydroborate; In tetrahydrofuran; water; at 20 ℃; for 3h; Catalytic behavior;
|
84 %Chromat. |
ethyl 4-nitrobenzoate
4-nitro-benzoic acid-(2,2,2-trichloro-ethyl ester)
2-(diethylamino)ethyl 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate
ethanol
ethyl 4-
ethyl 4-
4-(2-mercapto-ethylamino)-benzoic acid ethyl ester
ethyl 4-(N-butylamino)benzoate